A lumbar microdiscectomy is performed relieve leg pain from a pinched nerve in your lower back
What is a Discectomy?
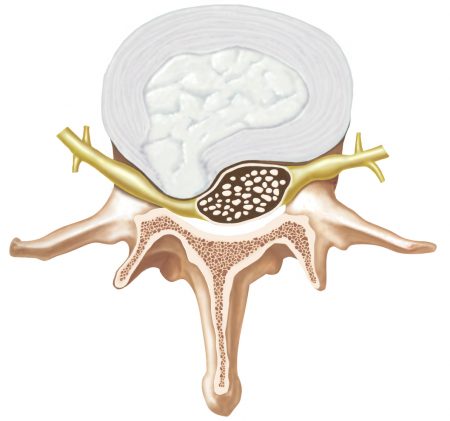
A discectomy is a surgery performed to relieve nerve-root compression that is caused by a herniated or bulging disc.
It can be performed as open surgery or as a minimally invasive procedure through an operative tube.
Discs are the cushions between the vertebral bodies (building blocks) of the spine. Each is composed of an exterior shell of tough cartilage, and a center of softer, more gelatinous material.
Through aging, normal wear and tear, or injury, the disc may bulge between the vertebrae. If it herniates (ruptures), it can cause severe pain by putting pressure on adjacent nerves, and decompression surgery may be required.
A microdiscectomy involves removing a small amount of bone and ligament in order to remove the small fragment of disc that pushes against a nerve..
Candidates for a Microdiscectomy
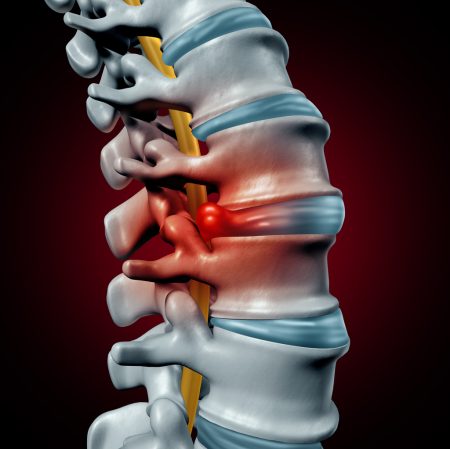
A microdiscectomy may be recommended for patients with an ongoing redicular paint (traveling down the leg). Typically, patients become candidates for surgery when more conservative methods have failed to resolve symptoms after a period of 6 weeks to 3 months. Before surgery is recommended, the following treatments are usually tried:
- Lifestyle changes (such as diet and exercise)
- Medications (such as analgesics and NSAIDs)
- Physical therapy
- Chiropractic treatment
- Epidural injections of corticosteroids
Certain neurological symptoms, such as weakness, numbness, or bladder or bowel dysfunction, especially if they occur suddenly, may necessitate emergency surgery.
Open vs Minimally Invasive Microdiscectomy
An open discectomy usually still involves a small midline incision, where the disc herniation is removed often times by using an operative microscope.
Advantage – A small incision is still small, but allowing more visualization of the surrounding anatomy and structures.
A minimally invasive microdiscectomy is usually done through a 3 cm incision using an operative tube and serial dilator system.
Advantage – The muscle is not cut, but rather spread out of the way by the serial dilator system to reach the herniated disc. This causes less muscle spasm, thus less postoperative incisional pain.
Recovery and Limitations
- The patient is usually home the same day of surgery
- The patient is up walking the day of surgery, hopefully with no leg pain or significantly improved leg pain
- Numbness/tingling of the leg may linger for several days to weeks after surgery due to manipulation of the nerve during surgery
- The patient will have incisional pain that improves after several days, mostly due to the muscle spasm from muscle dissection during surgery.
- The patient has to avoid heavy lifting, bending, and twisting for 6 weeks to allow the incision to heal
- Usually the patient is able to return to work or activities with no restrictions around 6 weeks after surgery
Contact Us
Send a Message to Specialty Surgery Center of St. Louis
If you have any questions, concerns, or comments regarding the Specialty Surgery Center of St. Louis, please fill out the short contact form below.
